Slab On Ground
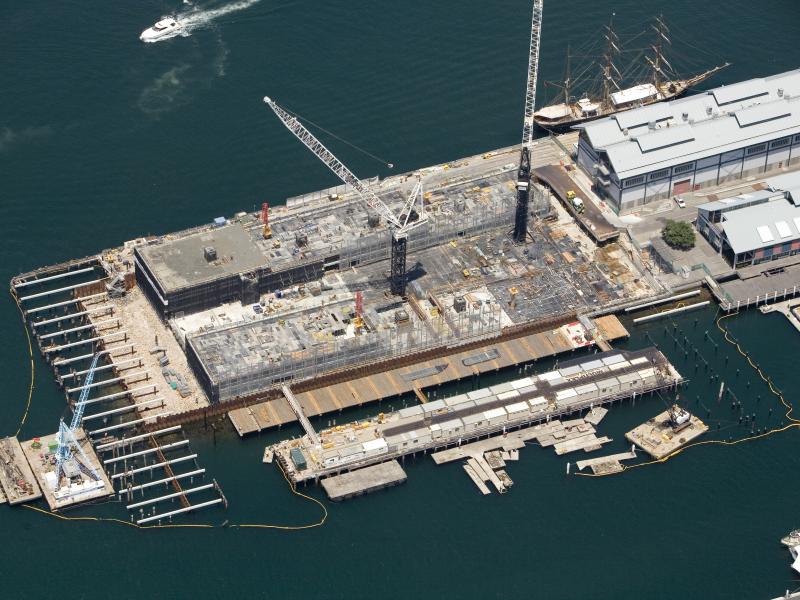
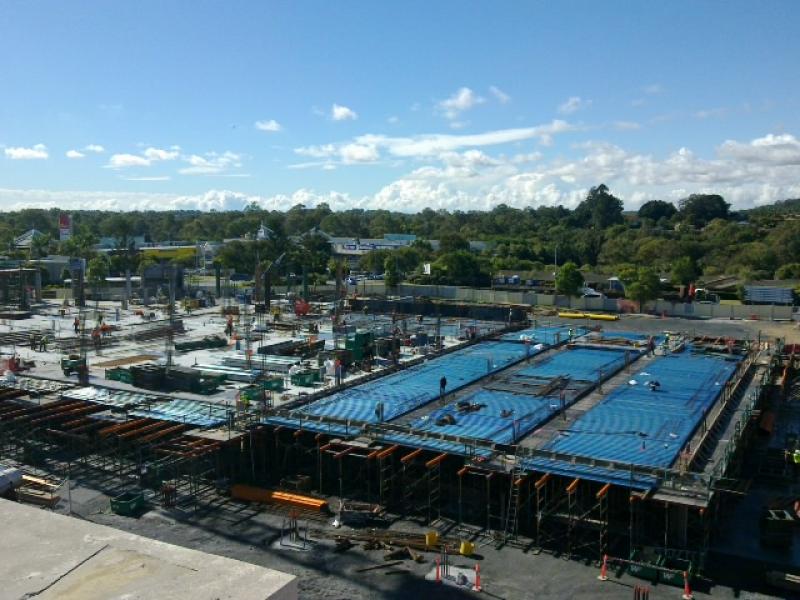
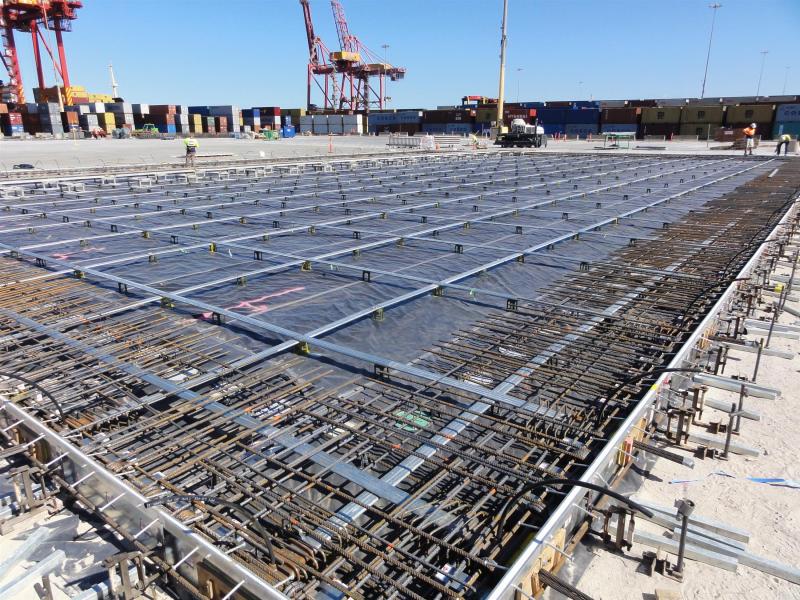
Slab On Ground
Post tensioning brings a number of unique benefits to the design and construction of slab on ground applications.
Common issues involved with the construction of slabs on ground include:
- Any mass pour concrete is subject to creep and shrinkage during curing, which can lead to cracking if uncontrolled.
- Slabs are particularly susceptible to cracking. The most common way to control this is with regular joints, either saw cuts or full expansion joints at typically 6-8m spacing.
- This leads to both large construction costs, up to 20% of initial construction value, and significant long-term maintenance costs.
- Joints also place limits on use of space.
By utilising a post tensioned slab on ground solution, the following benefits can be achieved:
- Significant reduction in joints bringing cost savings and improvements to operational performance, particularly in slabs with high traffic movement.
- Standard tendon lengths are 60m, compared to joint spacing of conventionally reinforced slab of 6-8m.
- 2,000-3,000sqm joint free pours are typical, up to 6,000sqm has also been achieved.
- Reduction in long term maintenance requirements due to reduced joint requirements, indicatively up to 60% cost saving.
- Increased loading capacity or reduction in slab thickness with significant material savings.
- Increased durability.
Typical applications for post-tensioning slabs on ground include:
- Logistics warehouses.
- Distribution centres.
- Bulk solid stores.
- Maintenance facilities.
- Refrigeration stores.
- Container handling facilities.
- Special applications.